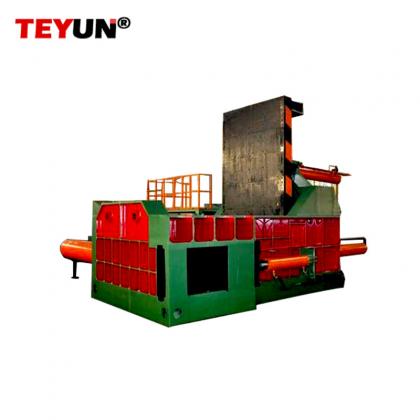
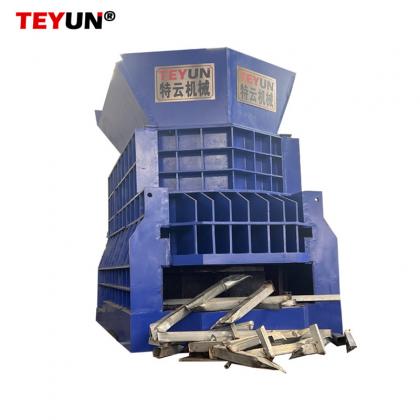
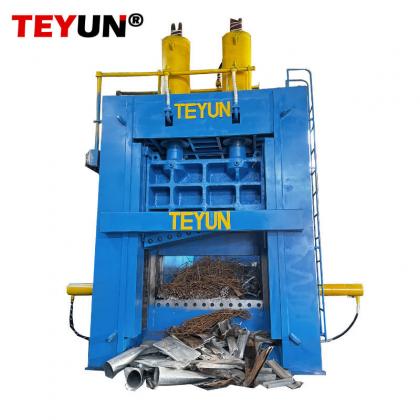
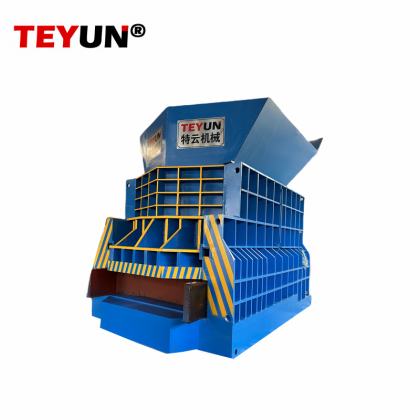
В основе современной инфраструктуры переработки лежит измельчитель металла — надежная машина, предназначенная для преобразования громоздкого лома в управляемые фрагменты. Эти промышленные рабочие лошадки играют ключевую роль в восстановлении ресурсов, обеспечивая эффективную переработку металлов для повторного использования. Разбивая все, от выброшенных автомобилей до бытовой техники, измельчители металла незаменимы в продвижении круговой экономики.
Механизм и принцип действия
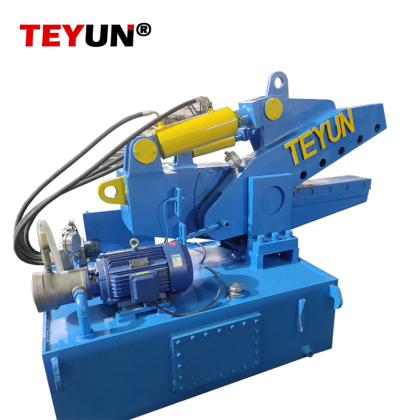
Металлические измельчители работают с использованием высокомоментных роторов, оснащенных закаленными стальными молотками или лезвиями, которые вращаются с огромной скоростью. Когда металлолом подается в камеру измельчителя, эти компоненты разрывают, разрезают и дробят материалы на более мелкие куски. Процесс часто включает несколько этапов: первоначальное измельчение, магнитное разделение для сортировки черных металлов (например, железа и стали) и передовые технологии сортировки для цветных металлов (например, алюминия, меди и латуни). Конечный продукт — измельченная металлическая «стружка» — имеет однородный размер, что облегчает плавку и переработку.
Универсальность в применении
Металлические измельчители обрабатывают различные материалы, включая отслужившие свой срок автомобили, строительный мусор, промышленное оборудование и электронные отходы. Например, переработка автомобилей в значительной степени зависит от измельчителей для извлечения стали из кузовов автомобилей, в то время как переработка электроники использует их для высвобождения драгоценных металлов из печатных плат. Измельченный металл впоследствии продается литейным заводам или производителям, которые переплавляют его для производства новых продуктов, что снижает зависимость от добычи первичной руды.
Экологические и экономические преимущества
Влияние измельчителей металла на окружающую среду огромно. Переработка металлов сохраняет природные ресурсы — например, добыча алюминия из бокситов требует на 95% больше энергии, чем переработка. Измельчители также убирают отходы со свалок, сокращая загрязнение и выбросы парниковых газов. С экономической точки зрения они генерируют доход, превращая лом в ценные товары. Торговля металлоломом, подпитываемая операциями по измельчению, формирует многомиллиардную мировую индустрию, поддерживая рабочие места в секторах переработки и производства.
Проблемы и инновации
Несмотря на свои преимущества, измельчители сталкиваются с трудностями. Загрязнители, такие как пластик или резина в потоках лома, могут усложнить переработку, требуя передовых систем сортировки. Техническое обслуживание является еще одной проблемой; абразивная природа металлов изнашивает компоненты, требуя регулярной замены. Безопасность остается первостепенной задачей, поскольку современные измельчители включают в себя такие функции, как механизмы аварийной остановки и автоматизированные системы подачи для защиты операторов.
Заглядывая вперед, инновации направлены на повышение эффективности и устойчивости. Гибридные и электрические измельчители снижают потребление энергии, в то время как системы сортировки на основе искусственного интеллекта повышают показатели извлечения материалов. Поскольку отрасли отдают приоритет декарбонизации, роль металлических измельчителей в обеспечении устойчивого производства металла будет только расти.
Заключение
Металлические измельчители — это больше, чем просто машины, они — катализаторы охраны окружающей среды. Превращая лом в повторно используемые ресурсы, они сокращают разрыв между отходами и производством, подчеркивая важность технологий в построении более зеленого будущего. По мере роста спроса на переработку непрерывное развитие технологий измельчения обеспечит постоянное использование металлов, продвигая вперед глобальные усилия по обеспечению устойчивости.

 Адрес : Mingjue Industry Park, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province
Адрес : Mingjue Industry Park, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province

 English
English français
français español
español العربية
العربية 日本語
日本語 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文















 Поддерживается сеть IPv6
Поддерживается сеть IPv6